What is a Star and Why Do THey Shine?
“For my part, I know nothing with any certainty, but the sight of the stars makes me dream.”
Vincent van Gogh
Today we’re exploring the fascinating world of stars. On a clear night, we can see countless stars in the sky. Some shine brightly, while others appear dim, like a sprinkle of cosmic dust that gently illuminates the night.
What is a Star?
- A star is a luminous object in space, made mostly of hydrogen and helium gas. Inside a star, hydrogen atoms fuse into helium through a process called nuclear fusion.
- This fusion releases enormous amounts of energy, which makes the star shine.
Check out my full video of this article below, or scroll down to continue reading the article.
How are Stars Born?
- Stars are born inside enormous clouds of gas and dust in space, known as nebulae. You may have seen breath-taking images of nebulae taken by the Hubble Space Telescope.
- Within these clouds, gravity pulls the gas and dust together, causing the cloud to collapse. As material falls inward, the core heats up.
- When the temperature reaches about 10 million kelvin, nuclear fusion begins. This fusion generates energy, creating pressure that balances gravity, allowing the star to stabilize.
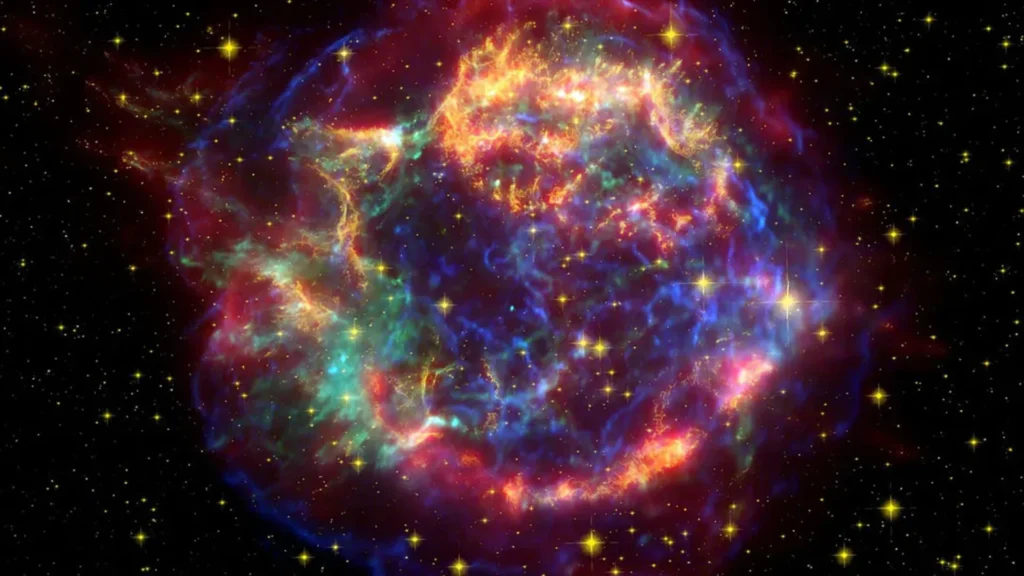

When a Star Dies
Eventually, every star will die. As thermodynamics teaches us, nothing lasts forever. When a star reaches the end of its life, one of three outcomes may occur, depending on its mass:
- Small to medium-sized stars (less than 8 solar masses) run out of fuel and cool down, becoming white dwarf stars. Over 97% of stars in our galaxy will end up as white dwarfs—small, dense, and faint stars. These stars can attract nearby matter, but if their mass exceeds 1.4 solar masses (the Chandrasekhar limit), they may explode in a type Ia supernova.
- Massive stars (8+ solar masses) burn through their fuel quickly. When the core collapses, it results in a supernova—one of the brightest events in the universe.
- If the remaining core is between 1.4 and 3 solar masses, it becomes a neutron star.
- If the core is more massive than 3 solar masses, gravity overwhelms all resistance, and it collapses into a black hole.
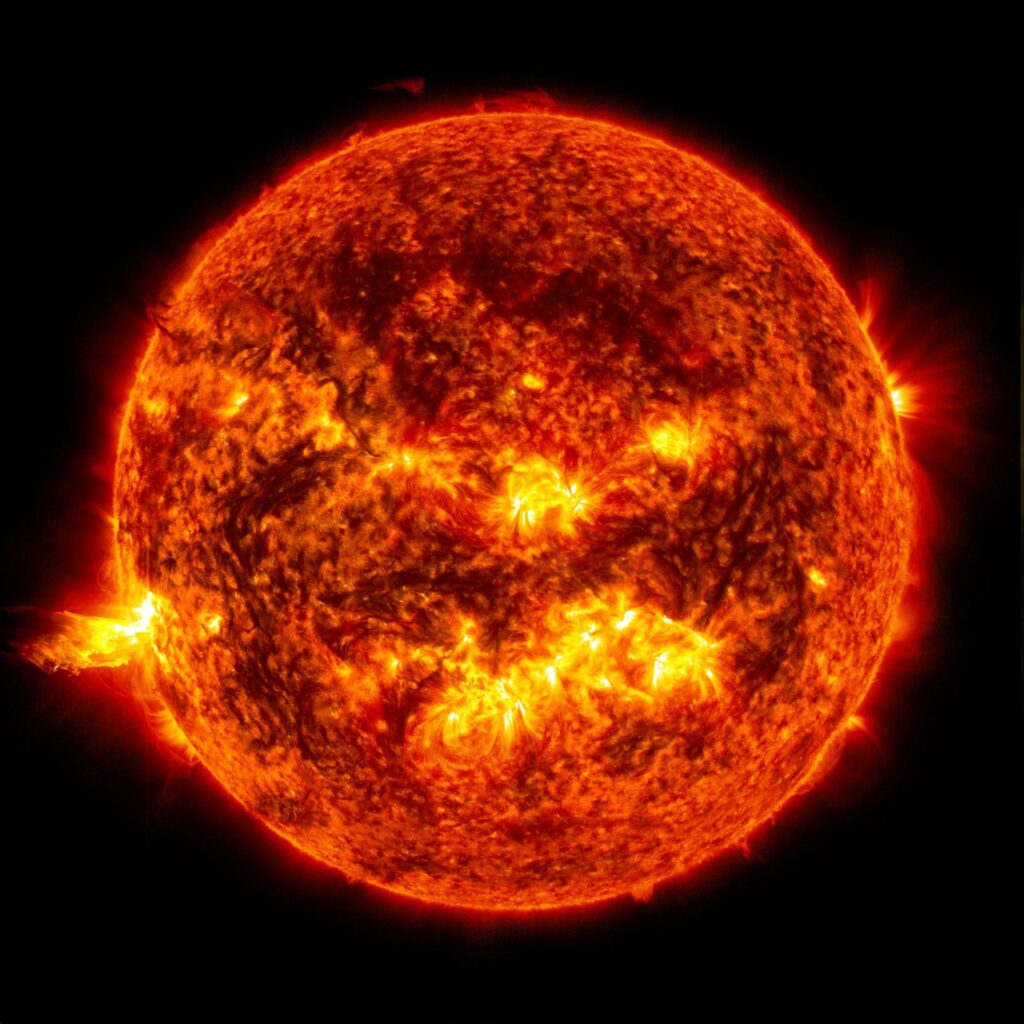
Facts About our Sun
- The Sun is the closest star to Earth. The distance from Earth to the Sun is called 1 Astronomical Unit (AU), equal to 149,597,870.7 km or about 93 million miles.
- Surface temperature: ~5,500°C
- Diameter: ~1,391,000 km
- It contains about 98.8% of the total mass of the Solar System.
- The next closest star is Proxima Centauri, located 4.25 light-years away in the constellation Centaurus. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year—about 63,241 AU.
Mysteries About Stars
- Why do some massive stars fail to explode as supernovae and instead collapse directly into black holes? Not all massive stars end their lives in a bright explosion. Some simply vanish, becoming black holes silently. Why this happens in some cases, but not others, is still a mystery.
- Why do some stars spin so fast? Certain stars (e.g., Be stars) rotate at incredibly high speeds- close to their breakup point. What causes such extreme rotation is still not fully understood.
Resources
The following books helped with my research for this article:
- Almost Everyone’s Guide to Science – John Gribbin
- Astrophysics for People in a Hurry – Neil deGrasse Tyson
Please note: I carefully research each topic before publishing; however, some facts may evolve as science advances. I appreciate your understanding and encourage readers to double-check key details. All articles are thoroughly researched and inspired by published works. article.
Please be kind, and have a nice day!
Nyx Log, Stardate 25081.4


thanks